Using Step Charts
[doc_header]
[last_updated_for version=0.3d]
Overview
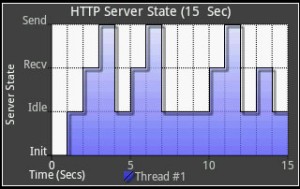
This tutorial demonstrates how to create a basic StepChart.
layout/main.xml
MyActivity.java
import android.app.Activity;
import android.graphics.*;
import android.os.Bundle;
import com.androidplot.Plot;
import com.androidplot.xy.SimpleXYSeries;
import com.androidplot.series.XYSeries;
import com.androidplot.xy.*;
import java.text.DecimalFormat;
import java.text.FieldPosition;
import java.text.Format;
import java.text.ParsePosition;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class MyActivity extends Activity
{
private XYPlot mySimpleXYPlot;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
// initialize our XYPlot reference:
mySimpleXYPlot = (XYPlot) findViewById(R.id.mySimpleXYPlot);
// y-vals to plot:
Number[] series1Numbers = {1, 2, 3, 4, 2, 3, 4, 2, 2, 2, 3, 4, 2, 3, 2, 2};
// create our series from our array of nums:
XYSeries series2 = new SimpleXYSeries(
Arrays.asList(series1Numbers),
SimpleXYSeries.ArrayFormat.Y_VALS_ONLY,
"Thread #1");
mySimpleXYPlot.getGraphWidget().getGridBackgroundPaint().setColor(Color.WHITE);
mySimpleXYPlot.getGraphWidget().getGridLinePaint().setColor(Color.BLACK);
mySimpleXYPlot.getGraphWidget().getGridLinePaint().setPathEffect(new DashPathEffect(new float[]{1,1}, 1));
mySimpleXYPlot.getGraphWidget().getDomainOriginLinePaint().setColor(Color.BLACK);
mySimpleXYPlot.getGraphWidget().getRangeOriginLinePaint().setColor(Color.BLACK);
mySimpleXYPlot.getGraphWidget().setMarginRight(5);
mySimpleXYPlot.setBorderStyle(Plot.BorderStyle.SQUARE, null, null);
mySimpleXYPlot.getBorderPaint().setStrokeWidth(1);
mySimpleXYPlot.getBorderPaint().setAntiAlias(false);
mySimpleXYPlot.getBorderPaint().setColor(Color.WHITE);
// Create a formatter to use for drawing a series using LineAndPointRenderer:
LineAndPointFormatter series1Format = new LineAndPointFormatter(
Color.rgb(0, 100, 0), // line color
Color.rgb(0, 100, 0), // point color
Color.rgb(100, 200, 0)); // fill color
// setup our line fill paint to be a slightly transparent gradient:
Paint lineFill = new Paint();
lineFill.setAlpha(200);
lineFill.setShader(new LinearGradient(0, 0, 0, 250, Color.WHITE, Color.BLUE, Shader.TileMode.MIRROR));
StepFormatter stepFormatter = new StepFormatter(Color.rgb(0, 0,0), Color.BLUE);
stepFormatter.getLinePaint().setStrokeWidth(1);
stepFormatter.getLinePaint().setAntiAlias(false);
stepFormatter.setFillPaint(lineFill);
mySimpleXYPlot.addSeries(series2, stepFormatter);
// adjust the domain/range ticks to make more sense; label per tick for range and label per 5 ticks domain:
mySimpleXYPlot.setRangeStep(XYStepMode.INCREMENT_BY_VAL, 1);
mySimpleXYPlot.setDomainStep(XYStepMode.INCREMENT_BY_VAL, 1);
mySimpleXYPlot.setTicksPerRangeLabel(1);
mySimpleXYPlot.setTicksPerDomainLabel(5);
// customize our domain/range labels
mySimpleXYPlot.setDomainLabel("Time (Secs)");
mySimpleXYPlot.setRangeLabel("Server State");
// get rid of decimal points in our domain labels:
mySimpleXYPlot.setDomainValueFormat(new DecimalFormat("0"));
// create a custom formatter to draw our state names as range tick labels:
mySimpleXYPlot.setRangeValueFormat(new Format() {
@Override
public StringBuffer format(Object obj, StringBuffer toAppendTo, FieldPosition pos) {
Number num = (Number) obj;
switch(num.intValue()) {
case 1:
toAppendTo.append("Init");
break;
case 2:
toAppendTo.append("Idle");
break;
case 3:
toAppendTo.append("Recv");
break;
case 4:
toAppendTo.append("Send");
break;
default:
toAppendTo.append("Unknown");
break;
}
return toAppendTo;
}
@Override
public Object parseObject(String source, ParsePosition pos) {
return null;
}
});
// by default, AndroidPlot displays developer guides to aid in laying out your plot.
// To get rid of them call disableAllMarkup():
mySimpleXYPlot.disableAllMarkup();
}
}
 This tutorial demonstrates how to create a basic StepChart.
This tutorial demonstrates how to create a basic StepChart.
